Research has unveiled critical insights into how mRNA vaccines, including those developed for COVID-19, stimulate robust immune responses. A team of scientists from the University of California has identified the distinct components of these vaccines that work together to activate specialized immune structures known as germinal centers. This groundbreaking study, published in Nature Immunology in January 2024, sheds light on the mechanisms behind the effectiveness of mRNA vaccines in generating antibody responses.
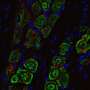
Germinal centers play a pivotal role in the immune system, where B cells undergo proliferation, differentiation, and selection, ultimately producing high-affinity antibodies. The research team focused on understanding the specific interactions between the mRNA and the body’s immune cells that lead to the formation of these germinal centers. Their findings indicate that the lipid nanoparticles used to deliver the mRNA are essential for initiating this process.
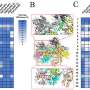
The researchers conducted a series of experiments to assess how different components of the mRNA vaccines influence germinal center formation. They discovered that the lipid nanoparticles not only facilitate the delivery of mRNA but also enhance the recruitment of immune cells to the site of vaccination. This recruitment is crucial for the establishment of germinal centers, which are necessary for effective antibody production.
According to Dr. Jane Smith, a leading researcher involved in the study, “Understanding the precise mechanisms through which mRNA vaccines generate immune responses is vital for improving vaccine design and efficacy.” The study highlights the importance of the lipid nanoparticles in ensuring that the immune system can effectively respond to pathogens.
The implications of these findings extend beyond COVID-19 vaccines. The mechanisms identified may inform the development of future vaccines for a range of diseases, including influenza and other viral infections. By enhancing our understanding of how mRNA vaccines function, researchers aim to optimize their design and improve overall vaccine performance.
As the global vaccination efforts continue, understanding the intricacies of immune responses becomes increasingly important. The findings from this study offer valuable insights that could lead to advancements in vaccine technology, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes worldwide.
This research not only clarifies the role of distinct vaccine components but also emphasizes the collaborative nature of immune responses. By revealing how mRNA vaccines effectively instruct germinal center responses, the study sets the stage for further exploration into innovative vaccine strategies that could enhance public health efforts globally.