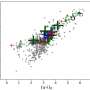
Astronomers using the Anglo-Australian Telescope (AAT) have made significant observations regarding the galactic globular cluster known as NGC 6569. Their findings, published on December 22, 2023, reveal that this cluster is actively losing stars due to a phenomenon called tidal stripping.
Globular clusters are dense collections of stars that orbit galaxies. In the case of NGC 6569, located approximately 30,000 light-years from Earth, the research indicates that gravitational interactions with the surrounding galaxy are causing it to shed stars. This process, known as tidal stripping, occurs when a larger gravitational body exerts a force on a smaller cluster, pulling stars away.
The study highlights how NGC 6569 is not an isolated case; many globular clusters experience similar fates. The research team utilized the AAT to conduct a detailed analysis of the cluster’s composition and structure. Their observations showed a noticeable reduction in the number of stars within NGC 6569, suggesting that the cluster is undergoing significant changes.
Understanding tidal stripping is crucial for astronomers as it provides insights into the dynamics of star clusters and their interactions with galaxies. This knowledge can enhance our comprehension of galaxy formation and evolution.
The data gathered from NGC 6569 gives astronomers a unique opportunity to study the effects of tidal forces on star clusters in real-time. The research team plans to continue monitoring NGC 6569 to further investigate the ongoing processes affecting its stellar population.
The findings contribute to a growing body of evidence regarding the complex interactions between galaxies and their globular clusters. As astronomers refine their techniques and tools, such as those employed by the AAT, they are better equipped to unveil the mysteries of the universe, including the fate of star clusters like NGC 6569.
In summary, the observations of NGC 6569 offer a glimpse into the dynamic processes that shape our universe. As research progresses, it is expected that more discoveries will emerge, helping to paint a clearer picture of cosmic evolution and the forces at play in the vast expanses of space.