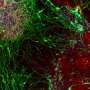
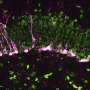
A groundbreaking study has unveiled critical genes essential for the transformation of embryonic stem cells into brain cells. This research, published on October 30, 2023, in the journal Nature Neuroscience, was led by Prof. Sagiv Shifman from The Institute of Life Sciences at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, in collaboration with Prof. Binnaz Yalcin from INSERM, France. Their findings highlight the intricate genetic requirements for early brain development and the potential implications of disruptions in this process.
The researchers employed a genome-wide CRISPR knockout screening method to systematically identify genes that play pivotal roles in brain cell differentiation. By targeting various genes, they were able to observe which ones are indispensable for the formation of neural cells during the embryonic stage. This innovative approach offers a comprehensive view of the genetic landscape essential for proper brain development.
The study revealed hundreds of genes that are critical for this transformation. Among these, several previously uncharacterized genes were identified, providing new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying brain development. The implications of these findings extend beyond basic science, as they may help in understanding various neurological disorders that arise from developmental anomalies. Researchers are particularly interested in how disruptions in these genes could lead to conditions such as autism and schizophrenia.
Understanding the genetic factors involved in brain cell differentiation is vital for advancing therapeutic strategies. As the research progresses, a clearer picture of how specific genes contribute to healthy brain development will emerge. This knowledge could pave the way for targeted interventions in cases where the development process is impaired.
The collaboration between teams from Israel and France underscores the importance of international research efforts in addressing complex biological questions. By sharing expertise and resources, these institutions have made significant strides in the field of neuroscience.
The findings from this study are expected to stimulate further research into gene function in brain development. As scientists continue to investigate these genetic requirements, the potential for discovering novel treatments for neurological diseases remains a promising avenue of inquiry.
This research not only advances our understanding of brain development but also sets the stage for future studies aimed at unraveling the complexities of the human brain. The ongoing exploration of gene functions in this context could ultimately lead to breakthroughs in medical science, enhancing our ability to tackle a range of cognitive disorders.