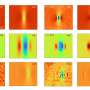
For the first time, physicists at the University of Milan, Italy, have successfully created a lump soliton, a remarkably stable packet of light waves that can navigate through three-dimensional space. This breakthrough allows these solitons to interact with one another while maintaining their distinctive shape, marking a significant advancement in the field of photonics.
The research team, led by Dr. Alessandro Rossi, published their findings in the European Physical Journal. Their work demonstrates how these solitons can sustain their form even when they collide with other solitons, a phenomenon that has intrigued scientists for decades. The stability of the lump soliton opens new possibilities for various applications, including advanced communication technologies and optical computing.
Understanding Lump Solitons
Solitons are unique wave formations that can travel indefinitely without dissipating. The creation of a lump soliton adds a new dimension to this concept by introducing stability in three-dimensional environments. Traditional solitons have been primarily studied in one or two dimensions, and the leap to three dimensions presents both challenges and opportunities for researchers.
Dr. Rossi explained that the experimental setup involved intricate laser systems and precise measurements. The team utilized advanced techniques to manipulate light waves, enabling the formation of these resilient packets. “Our results demonstrate the potential for solitons to be more than theoretical constructs; they can have practical applications in real-world technologies,” he noted.
The implications of this research extend beyond fundamental physics. As industries increasingly rely on sophisticated optical systems, the ability to create stable solitons could revolutionize how data is transmitted and processed.
Future Applications and Research Directions
The potential applications of lump solitons are vast. They could play a crucial role in developing next-generation optical fibers, enhancing data transmission capabilities. Additionally, their stability might lead to breakthroughs in quantum computing, where reliable information transfer is essential.
Research into solitons has gained momentum in recent years, with various universities and institutions worldwide exploring their properties. The work from the University of Milan not only contributes to this growing field but also sets the stage for further exploration of multi-dimensional solitons.
As this area of study evolves, scientists anticipate uncovering more about the interactions between different types of solitons. Understanding these interactions could lead to the development of new materials and technologies that harness the unique properties of light.
In conclusion, the creation of the lump soliton by Italian physicists is a landmark achievement in the realm of optics. It not only enhances the understanding of light wave behavior but also paves the way for innovative applications that could transform the technology landscape in the coming years.