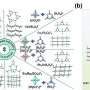
Researchers have successfully developed high-performance fluoroborate crystals that could significantly enhance the functionality of deep-ultraviolet (DUV) lasers. These lasers, which operate at wavelengths below 200 nanometers, are crucial for various applications including material analysis and lithography in both scientific research and industrial manufacturing.
The advancement of DUV lasers is heavily reliant on the availability of robust nonlinear optical (NLO) crystals. These crystals must meet strict criteria to be effective. Specifically, they need to exhibit large second harmonic generation (SHG) responses, moderate birefringence, and wide bandgaps. Achieving this balance has posed challenges for scientists and engineers in the field.
Significance of the Development
The introduction of these fluoroborate crystals marks a pivotal step in making DUV lasers more commercially viable. Currently, many existing NLO crystals fall short of the performance requirements needed for widespread use. The new materials developed by researchers offer a promising solution, potentially revolutionizing the manufacturing processes in industries such as semiconductor production and advanced materials development.
These advancements are expected to facilitate improvements in laser efficiency and capability, ultimately leading to more precise and effective applications in both research and commercial settings. The integration of these crystals into existing technologies could streamline processes and reduce production costs, making DUV lasers more accessible to a broader range of industries.
Future Implications and Research Directions
As the demand for more efficient and powerful lasers continues to rise, the ongoing research into fluoroborate crystals will likely lead to further innovations in optical technology. Scientists are now exploring additional properties of these crystals to enhance their performance even further.
The implications of this research extend beyond traditional applications. Emerging fields such as quantum computing and advanced photonics may benefit significantly from improved DUV laser technology. The ability to manipulate light at such small wavelengths opens up new avenues for research and development that could lead to groundbreaking discoveries.
In conclusion, the development of high-performance fluoroborate crystals represents a significant milestone in the field of nonlinear optics. As researchers continue to refine these materials, the future of DUV lasers looks promising, with potential impacts across various industries and scientific disciplines.