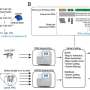
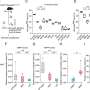
Recent research from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has uncovered significant insights into how neurons diversify despite originating from the same DNA. This study highlights the role of RNA editing in shaping the unique characteristics of individual neurons within the brain and body.
Neurons, essential cells in the nervous system, acquire distinct identities through the selective transcription of genes into RNA. The MIT study reveals that these individual cells edit specific sites within their RNA transcripts at varying rates, contributing to their diversity. This RNA editing process is vital for determining the type of neuron each cell will become, showcasing a complex layer of regulation in neuronal development.
Understanding RNA Editing’s Impact on Neuron Identity
The research demonstrates that the differences in RNA editing can lead to a wide array of neuronal types, which play crucial roles in brain function and overall physiology. Each neuron edits its RNA transcripts differently, indicating a level of individuality among cells that is more nuanced than previously understood.
The findings emphasize how variations in gene expression and RNA editing can influence neuronal properties, potentially affecting how neurons communicate and function within neural circuits. This has broader implications for understanding neurological disorders, as disruptions in RNA editing may contribute to conditions such as autism and schizophrenia.
The study represents a significant advancement in neuroscience, illustrating the dynamic processes that govern neural diversity. By identifying specific mechanisms of RNA editing, researchers at MIT are paving the way for potential therapeutic strategies aimed at correcting or compensating for the effects of improper RNA function.
Overall, this research underscores the importance of RNA beyond its traditional role as a messenger between DNA and proteins. The ability of neurons to edit RNA transcripts offers new avenues for exploration in both basic neuroscience and the development of targeted treatments for neurological diseases. As the field continues to evolve, the intricate relationship between RNA editing and neuronal identity will undoubtedly remain a focal point of scientific inquiry.