Across Europe, communities are confronting a troubling legacy of soil contamination. Recent initiatives have emerged to identify and mitigate the impact of invisible pollutants, particularly per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). These efforts reflect a growing awareness about the health risks associated with contaminated soil and are driven by both scientific research and grassroots activism.
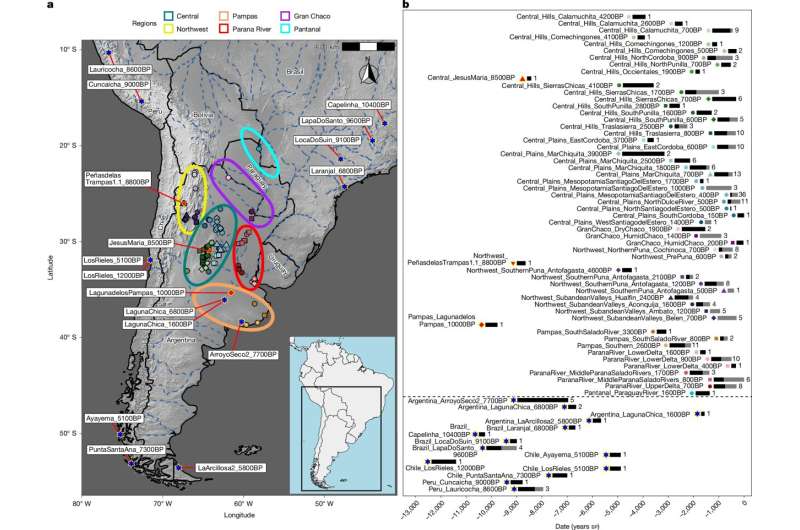
In Denmark, the first PFAS crisis has prompted urgent action from both government and citizens. Following alarming reports about drinking water contamination, the Danish government is now investing in extensive soil mapping projects. This initiative aims to uncover the extent of PFAS pollution, which has been linked to various health issues, including cancer and liver damage. The European Environment Agency (EEA) has indicated that such pollutants are not isolated to Denmark; they pose a widespread risk across the continent.
Innovative Mapping Initiatives Across Europe
Countries are adopting new technologies to create comprehensive maps of soil quality. For instance, the European Commission has launched a series of soil mapping initiatives designed to provide detailed assessments of contamination levels. These projects utilize advanced geospatial technologies and satellite imagery, enabling researchers to visualize pollution patterns that were previously undetectable.
According to a report by the EEA in 2023, up to 40% of European soils are affected by some form of contamination. This statistic underscores the urgent need for action. The maps generated from these initiatives will not only inform policy but also empower local communities to advocate for cleaner environments.
Grassroots organizations are also playing a crucial role in this movement. Citizens are collaborating with scientists to conduct their own soil tests, raising awareness about hidden pollutants. These collaborations often lead to local campaigns aimed at improving soil health and enhancing regulatory measures.
Health Risks and Environmental Impact
The health implications of soil pollution are significant. Research indicates that long-term exposure to PFAS can lead to serious health issues, including developmental problems in children and increased cholesterol levels. The International Union of Soil Sciences emphasizes the need for public awareness and education regarding these dangers, as many people remain unaware of the risks associated with contaminated soil.
Local governments are responding by implementing stricter regulations on waste disposal and industrial practices. The European Union is also exploring legislative measures to curb the use of harmful substances. This regulatory framework aims to protect public health and preserve the environment for future generations.
As the movement to combat soil pollution gains momentum, more countries are likely to follow Denmark’s lead. The integration of scientific research, community involvement, and policy reform forms a robust strategy against a problem that has long been overlooked.
The momentum generated by these initiatives serves as a reminder of the importance of vigilance in environmental stewardship. By addressing soil pollution head-on, Europe is paving the way for a cleaner, healthier future. The ongoing efforts not only aim to protect the land but also to ensure that citizens can trust the safety of their food and water sources moving forward.
The journey to map and mitigate soil pollution is far from over, but the steps being taken today will undoubtedly shape the landscape of environmental policy in the years to come.