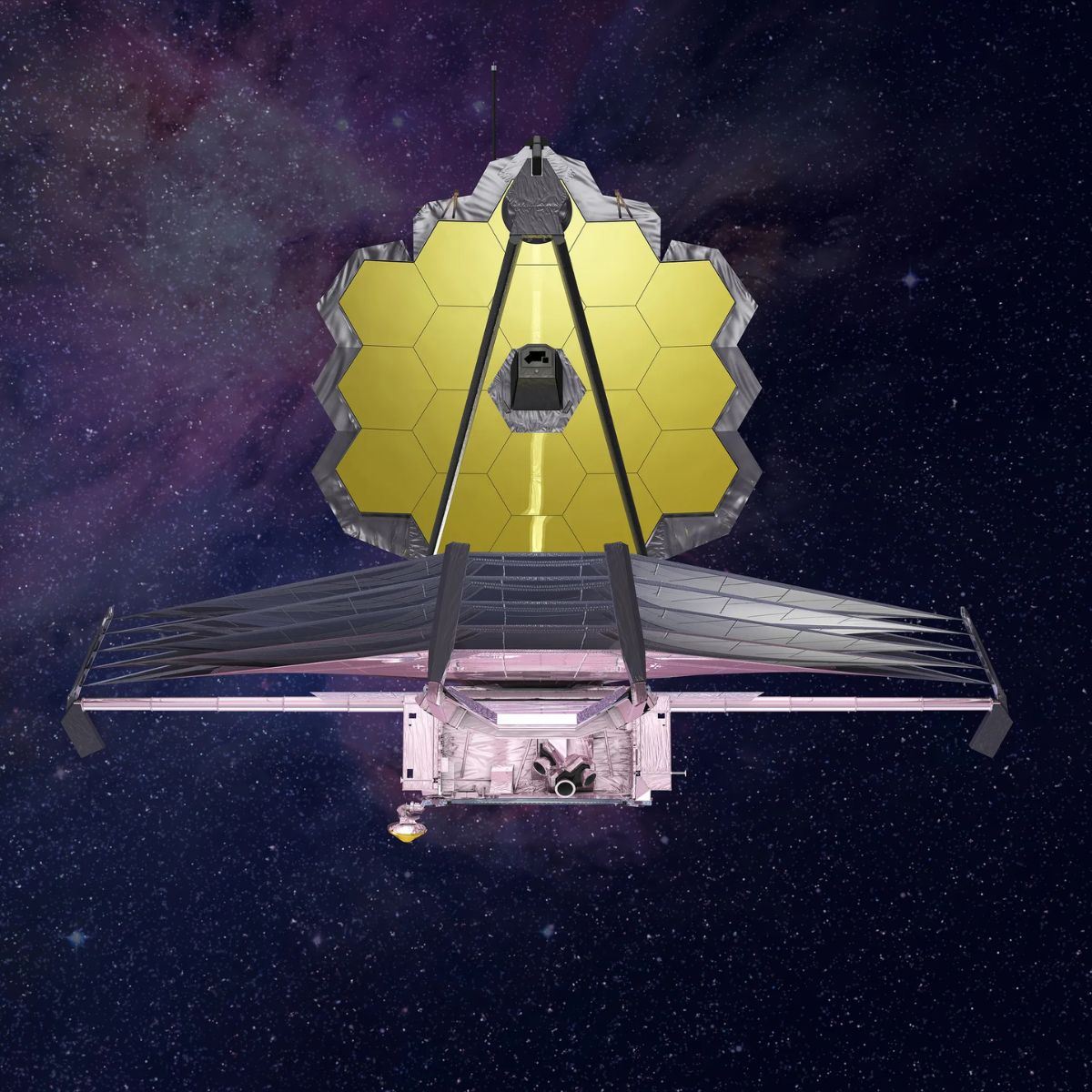
Astrophysicists have made a groundbreaking discovery, locating a supermassive black hole in the early universe that is growing at an astonishing rate. This finding, revealed by the James Webb Space Telescope and reported by the European Space Agency (ESA), offers new insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies.
The black hole, identified as existing just 1.5 billion years after the Big Bang, is notable not only for its size but for its unexpected growth rate. This discovery challenges existing theories about the pace at which supermassive black holes can accumulate mass in the early stages of the universe. The findings suggest that these cosmic giants may have developed much faster than previously thought.
Implications for Cosmic Evolution
The implications of this discovery are significant. Astronomers have long debated how supermassive black holes formed and grew so quickly in the early universe. The existence of such a rapidly growing black hole raises questions about the conditions that allowed for its formation. It also suggests that the mechanisms of galaxy formation may be more complex than current models indicate.
This particular black hole is located in a galaxy that is undergoing intense star formation, which may provide the necessary material for its growth. According to the ESA, this finding underscores the importance of studying the early universe to understand how galaxies and their central black holes evolve together.
The research team utilized the advanced capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope to observe this black hole in detail. The telescope’s ability to capture infrared light allows astronomers to peer through cosmic dust and gas, providing clearer images and data about distant celestial objects. This technology is crucial for uncovering the mysteries of the universe’s infancy.
Future Research Directions
As scientists continue to analyze the data from the James Webb Space Telescope, they expect to refine their understanding of black hole growth and galaxy formation. Future research will focus on measuring the black hole’s mass and studying its surrounding environment to gain further insights into its rapid growth.
The discovery of this supermassive black hole not only enhances our knowledge of cosmic history but also highlights the capabilities of modern astronomical technology. As more data is collected, the scientific community anticipates further revelations that could reshape our understanding of the universe’s evolution. Observations like these will be pivotal in answering fundamental questions about how supermassive black holes influence their host galaxies and the larger cosmos.
This extraordinary finding exemplifies the power of collaboration in space research. The James Webb Space Telescope, a joint venture between NASA, ESA, and the Canadian Space Agency, is set to continue its mission, exploring the depths of space and uncovering the secrets of our universe. The ongoing research promises to keep pushing the boundaries of what we know about black holes and their role in shaping the cosmos.