Recent research at Harvard University has shed light on the effects of the psychedelic compound dimethyltryptamine (DMT) on the human sense of self. Users of DMT report a temporary dissolution of self-identity, which raises intriguing questions about the nature of consciousness and self-awareness.
DMT, a potent psychedelic found in various plants and animals, produces profound alterations in perception. This research suggests that DMT interacts with brain activity linked to self-referential processes, specifically through the modulation of alpha waves. Alpha waves are oscillations in brain activity typically associated with relaxation and calmness. The connection between these waves and self-awareness during DMT experiences, however, remains unclear.
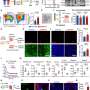
The study involved observing brain activity in individuals under the influence of DMT. Researchers monitored changes in brain wave patterns and assessed participants’ subjective experiences of self. Preliminary findings indicate a significant decrease in activity in regions of the brain responsible for maintaining the sense of self, suggesting that DMT may facilitate a temporary state of ego dissolution.
Understanding the Brain’s Self-Referential Network
The research highlights the importance of understanding how psychedelics like DMT can alter the brain’s typical processes. According to lead researcher Dr. Samantha Lee, “Our findings indicate that DMT may disrupt the neural networks related to self-referential thought, leading to a unique experience of consciousness.” This insight may have implications for therapeutic applications, particularly in treating conditions such as depression and anxiety, where the sense of self can become distorted.
DMT’s effects on the brain are complex and not fully understood. Previous studies have suggested that psychedelics can increase connectivity between different brain regions. This increased connectivity may contribute to the subjective experience of unity and connectedness often reported by users. Research into DMT and similar compounds could further illuminate the intricacies of human consciousness and the mechanisms underlying self-awareness.
Potential Therapeutic Applications
As interest in psychedelic therapy grows, the implications of this research could pave the way for innovative treatment strategies. The potential to utilize DMT in a controlled environment may offer new avenues for mental health treatment. Experts are advocating for continued exploration of psychedelics in clinical settings, emphasizing the importance of understanding the mechanisms that drive their effects.
In March 2024, researchers plan to present their findings at an international neuroscience conference, drawing attention to the need for further investigation into DMT’s impact on self-perception. By illuminating the connections between brain activity and the sense of self, this research may contribute to a broader understanding of consciousness itself.
As the field of psychedelic research evolves, the exploration of compounds like DMT will likely continue to challenge and reshape our understanding of the human mind. As scientists delve deeper into the connections between brain activity and self-awareness, the potential for transformative insights into the nature of consciousness remains vast.