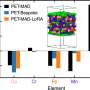
A research team led by Prof. Ye Jichun from the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE), part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has achieved a significant milestone in solar technology. They have developed a method that enhances the efficiency of industrial tunnel oxide passivating contact (TOPCon) solar cells to an impressive 26.09%, while simultaneously reducing silver usage and improving bifacial power generation performance.
This innovative approach addresses critical challenges facing the solar industry, combining cost-effectiveness with high efficiency. The team’s findings indicate that the new design not only maximizes energy output but also minimizes material costs, an essential factor in making solar technology more accessible globally.
Innovative Techniques and Collaboration
The research is the result of collaborative efforts among various partners, emphasizing the importance of teamwork in advancing technological solutions. By integrating a synergistic technical solution, the team was able to optimize the performance of TOPCon solar cells. This method involves a unique combination of materials and structural design that enhances light absorption and energy conversion.
A notable aspect of this development is the reduction in silver usage, a precious metal that significantly increases the cost of solar cell production. By minimizing reliance on silver, the researchers have created a more sustainable product that can compete effectively in the market.
Implications for the Solar Industry
The implications of achieving a solar cell efficiency of 26.09% are far-reaching. High-efficiency solar cells can lead to greater energy production from the same surface area, making solar power a more viable option for both commercial and residential applications. This advancement is particularly important as the world increasingly turns to renewable energy sources to combat climate change.
Furthermore, the enhanced bifacial performance means that these solar cells can generate electricity from both sides, further increasing their energy output. This feature becomes crucial in maximizing the efficiency of installations in various environments.
As countries around the world set ambitious targets for renewable energy adoption, innovations like these will play a vital role in meeting energy demands sustainably. The research led by Prof. Ye Jichun represents a critical step forward in the ongoing evolution of solar technology, potentially paving the way for future advancements in the field.
This breakthrough not only highlights the capabilities of Chinese researchers but also reinforces the global push towards more efficient and environmentally friendly energy solutions. The findings from this study will likely inspire further research and development, fostering a new era of solar technology that prioritizes efficiency and sustainability.