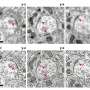
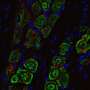
An international team of researchers has made significant strides in neuroscience by developing a groundbreaking imaging protocol that reveals the intricate connections between brain cells in mice. Led by the Francis Crick Institute in collaboration with the Paul Scherrer Institute, this innovative technique combines advanced X-ray imaging with radiation-resistant materials sourced from the aerospace industry. Their findings were published in the journal Nature Methods.
The new imaging protocol allows for a detailed examination of the mouse brain’s cellular architecture, opening the door to better understanding of various neurological conditions. The researchers utilized high-resolution X-ray imaging to visualize the complex networks formed by neuronal connections, providing insights that were previously difficult to obtain with traditional imaging techniques.
Innovative Approach Using Aerospace Materials
One of the standout features of this research is the incorporation of materials developed for the aerospace industry, which are particularly resistant to radiation. This adaptation enables the imaging process to be more effective and to produce clearer results. The team believes that this method could eventually be applied to human studies, offering potential breakthroughs in understanding human brain disorders.
By capitalizing on the unique properties of these materials, the researchers have enhanced the resolution of the images captured, allowing them to identify and analyze connections in the mouse brain that were once too subtle to detect. The implications of this work are vast, as they could provide a clearer understanding of the underlying mechanisms of diseases such as Alzheimer’s and autism.
Potential Impact on Neuroscience Research
This advancement marks a significant milestone in neuroscience research. The ability to visualize brain cell connections with such precision can transform the field, enabling scientists to explore the brain’s functioning in unprecedented detail. With the publication of their work in Nature Methods in 2023, the team hopes to inspire further research and collaboration in the field.
The researchers emphasize the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in achieving such breakthroughs. By merging expertise from neuroscience and advanced materials science, they have developed a tool that could significantly enhance our understanding of brain connectivity and its implications for health and disease.
In conclusion, this innovative X-ray imaging technique represents a promising step forward in mapping the complexities of the mouse brain. As researchers continue to explore its potential applications, the scientific community eagerly anticipates the insights that may emerge from this pioneering work.