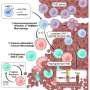
Researchers at Purdue University have made a significant discovery regarding the mechanism behind twisted growth in plants. This phenomenon, observed in various species, enables plants to navigate obstacles in their environment. Whether it’s morning glories spiraling up fence posts or grape vines corkscrewing through arbors, twisted growth serves as a vital adaptation tool in the plant kingdom.
The study, published in the journal Nature Plants, reveals that roots often exhibit this twisting behavior to avoid rocks and other debris buried in the soil. This ability allows plants to efficiently search for water and nutrients, which are essential for their growth and survival. The findings highlight a previously unexplored aspect of plant behavior and could have implications for agricultural practices.
Understanding the Mechanism of Twisted Growth
The research team utilized advanced imaging techniques to observe and analyze the growth patterns of various plants. They discovered that certain genetic factors and environmental stimuli trigger the twisting behavior. By manipulating these variables in controlled experiments, the researchers were able to document how roots change direction in response to obstacles.
According to lead researcher Dr. Sarah Johnson, “This work opens up new avenues for understanding how plants adapt to their environments. By identifying the genetic pathways involved in twisted growth, we can explore ways to enhance crop resilience.” The implications of this research could be particularly beneficial in areas facing soil fragmentation or other challenges to plant growth.
The team also found that the twisting mechanism plays a crucial role in the overall health of the plant. By allowing roots to navigate around barriers, plants can optimize their root systems, leading to improved nutrient uptake. This discovery may lead to innovative methods for enhancing agricultural yields and crop sustainability.
Implications for Agriculture and Future Research
This breakthrough provides valuable insights for the agricultural sector, especially in regions where soil conditions are less than ideal. By applying the knowledge gained from this research, farmers could potentially develop crops that are better equipped to thrive in challenging environments.
Furthermore, the study encourages further exploration into the genetic aspects of plant behavior. Understanding the specific genes involved in twisted growth may pave the way for genetic engineering approaches aimed at improving crop resilience against climate change and other environmental stressors.
As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of plant growth, this discovery underscores the importance of studying plant adaptability. With an increasing global focus on sustainable farming practices, the insights gained from this research could lead to significant advancements in how we cultivate crops for future generations.