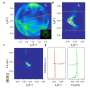
A recent study published in Economic Inquiry has uncovered significant insights into how immigration attitudes evolve within communities and subsequently influence neighboring areas. Researchers found that the language used by media and the dynamics of social networks play a critical role in shaping these political attitudes.
The study highlights a concerning trend: as local attitudes toward immigration shift, these changes can ripple through surrounding communities. This phenomenon underscores the interconnectedness of social sentiments, revealing that public opinion is not isolated but rather part of a larger network influenced by various factors, including media portrayal.
Media Language’s Influence on Perceptions
The researchers conducted an extensive analysis of media reports and social media discussions surrounding immigration. They identified that certain linguistic choices can either exacerbate or alleviate negative perceptions of immigrants. For instance, framing immigrants as “threats” versus “contributors” significantly alters public sentiment.
This finding is crucial, as it emphasizes the power of language in fostering either divisive or inclusive narratives. The study suggests that when media outlets adopt more positive language regarding immigration, they can help create a more welcoming environment in local communities.
Furthermore, the role of social networks cannot be understated. As individuals share content and engage in discussions online, their views can influence those within their circles. This suggests that a shift in one locality’s attitudes may lead to changes in neighboring areas through shared social connections.
Implications for Policymakers and Media
The implications of this research are profound, particularly for policymakers and media organizations. Understanding how language affects public perception can guide more effective communication strategies. Policymakers can leverage these insights to foster community dialogues that promote understanding and inclusivity.
Moreover, media organizations are urged to consider the impact of their language choices. By adopting a more balanced and constructive approach to reporting on immigration, they can contribute positively to the public discourse.
The study presents a call to action for both sectors to embrace their roles in shaping societal attitudes. As immigration continues to be a pivotal issue globally, the need for thoughtful and responsible communication has never been more pressing.
In conclusion, as communities navigate the complexities of immigration, the findings from this study serve as a reminder of the powerful interplay between media language, social networks, and public attitudes. By recognizing and harnessing this influence, society can work towards a more informed and compassionate approach to immigration policy and discourse.