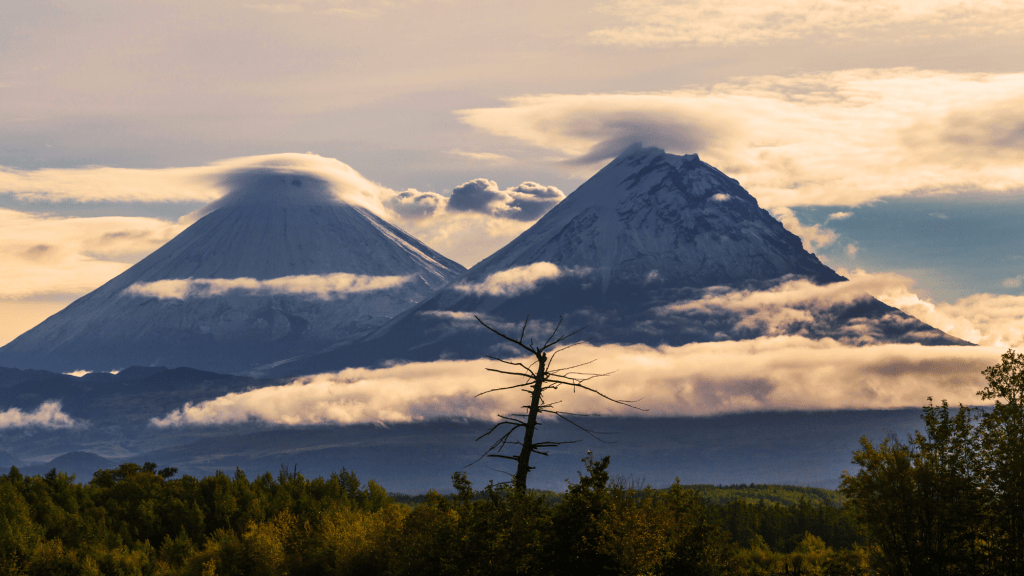
New reports confirm that Russia’s Bezymianny volcano is experiencing a dramatic resurgence, just 69 years after its catastrophic collapse. An ash plume recently reached an astonishing height of 32,800 feet during an eruption in November 2023, further accelerating the volcano’s remarkable recovery process. This event marks a significant milestone in its ongoing transformation on the Kamchatka Peninsula, a region notorious for its active volcanic activity.
The Institute of Volcanology and Seismology reported that Bezymianny’s latest eruption continues a story of rebirth that scientists have meticulously documented over decades. Once towering at least 10,213 feet before its 1956 explosion, the volcano has been steadily reconstructing its classic cone shape since the summit was obliterated, leaving behind a horseshoe-shaped crater.
Recent studies indicate that Bezymianny has been adding an impressive average of 26,400 cubic meters of rock each day since its collapse. Researchers now estimate the volcano could reach its pre-eruption height by as early as 2030 to 2035. Co-authors Alexander Belousov and Marina Belousova highlighted the rapid growth of the new volcanic structure, stating, “the most surprising thing was the fast growth of the new volcanic edifice.”
Despite this impressive recovery, scientists remain cautious. The unique horseshoe-shaped crater poses a risk for potential future collapses, which could trigger new explosive eruptions. The rebuilding process, while remarkable, serves as a reminder of the unpredictable nature of volcanic activity.
Bezymianny’s resurgence isn’t solely due to explosive ash events; ongoing fieldwork and aerial surveys show decades of effusive lava flows beginning in 1977. Observations indicate that as lava became less viscous and silica-rich, it spread more easily, contributing to the gradual restoration of the volcano’s height and symmetry.
Monitoring efforts are ongoing, utilizing satellites, ground stations, and webcams. The long history of collapse and rebirth not only informs scientists about Bezymianny but also aids in predicting the behavior of other volcanoes with similar histories, including the infamous Mount St. Helens.
Researchers anticipate continued growth and reshaping of Bezymianny in the near future. As the volcano’s remarkable journey unfolds, it serves as a vivid reminder of nature’s power and resilience. The geological community watches closely as Bezymianny writes the next chapters of its extraordinary recovery story, highlighting the urgent need for ongoing observation and research.
Stay tuned for further updates as this volcanic phenomenon continues to develop in real time.