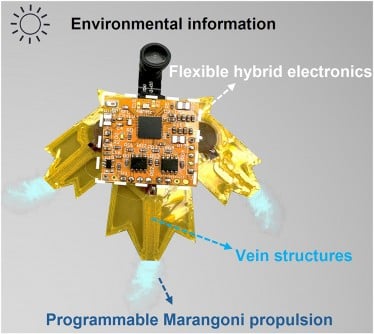
BREAKING NEWS: Researchers from the University of Macau and Huazhong University of Science and Technology have developed groundbreaking aquatic robots, dubbed “S-aquabots,” that could transform environmental monitoring and search-and-rescue missions. This innovative technology, powered by a Marangoni motor, was unveiled in a study published in the eScience journal on May 2025.
These centimeter-scale robots utilize ethanol-fueled propulsion, making them remarkably efficient and adaptable. Each S-aquabot can navigate for up to 226 seconds using just 1.2 mL of ethanol, covering distances of approximately 5 meters. This achievement represents a fuel efficiency improvement by 3.5 times, showcasing their potential for long-term deployment in environmental settings.
The S-aquabots, designed with a leaf-inspired structure, possess unique camouflage capabilities, allowing them to blend seamlessly with floating vegetation. This feature is crucial for ecological monitoring, as their nearly silent operation (only 40 dB, comparable to natural background noise) minimizes disturbance to wildlife.
Prof. Junwen Zhong, the study’s lead author, emphasized the importance of this technology:
“Our leaf-inspired S-aquabots demonstrate how biomimicry and advanced materials can overcome the long-standing challenges of aquatic robotics.”
He pointed out that the combination of programmable propulsion and flexible electronics allows for precise control and multifunctionality in untethered water robots.
Demonstrations of the S-aquabots included obstacle avoidance, pollutant collection, and real-time video transmission, illustrating their versatility. They can track pollutants, monitor water quality, and gather weather data, making them invaluable for environmental science and disaster response operations.
The integration of mini-cameras and digital sensors enables long-term environmental monitoring. The S-aquabots can record light intensity and air temperature over extended periods, enhancing their utility for researchers and conservationists alike.
As the world grapples with climate change and environmental degradation, the development of these advanced aquatic robots is a timely and significant advancement. Their silent operation and ability to operate autonomously position them as effective tools for ecological preservation.
Looking ahead, researchers are exploring the potential of integrating sustainable energy sources, such as solar cells, to extend the endurance of these robots, further enhancing their applicability in diverse aquatic environments.
This innovation not only marks a technological breakthrough but also serves as a blueprint for future intelligent, adaptable robotic systems aimed at supporting environmental protection and scientific research. As the capabilities of these S-aquabots develop, the implications for ecological monitoring and disaster response are profound, promising a new era of efficient and discreet environmental stewardship.
Stay tuned for more updates on this developing story as the implications of these versatile aquabots continue to unfold.