URGENT UPDATE: A groundbreaking review study from the Department of Civil Engineering at Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University in Türkiye has just been released, shedding light on essential methods for preserving historical structures. This comprehensive analysis, titled “Materials Characterization of Historical Structures: A Review,” aims to tackle significant challenges in cultural heritage preservation, which could affect the longevity of these irreplaceable assets.
The research highlights that understanding the properties of building materials, like natural stones and mortars, is critical for effective restoration efforts. With a lack of holistic analysis and clear guidance on characterization methods, conservation initiatives face serious obstacles. The study emphasizes the urgency of implementing robust analytical techniques to ensure the survival of our architectural heritage.
Among the study’s key findings is the utilization of various analytical methods categorized into four core areas. These include:
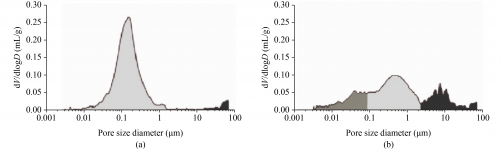
1. **Physical and Thermal Property Analysis:** Techniques such as **Mercury Intrusion Porosimetry (MIP)** and **Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)** are pivotal in determining material porosity and thermal resistance. For example, MIP reveals two main pore size distributions in mortars from Amaiur Castle, while TGA indicates that calcite decomposes between 600–900 °C, resulting in a mass loss of 20%–40%.
2. **Chemical Property Analysis:** Advanced techniques, including **X-ray Diffraction (XRD)** and **Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)**, allow researchers to qualitatively and quantitatively determine material components. Notably, high concentrations of lead and zinc were detected in the black crusts of Seville Cathedral, raising concerns about environmental impacts.
3. **Mechanical Property Analysis:** Non-destructive methods like **Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV)** and **Schmidt hammer tests** provide insights into the mechanical properties of historical structures without causing damage, ensuring their preservation for future generations.
4. **Visualization Techniques:** Methods such as **Scanning Electron Microscopy-Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS)** and **Infrared Thermography (IRT)** help identify hidden defects and material morphology, crucial for informed restoration efforts. For instance, IRT has successfully detected invisible cracks in Malatya Taşhoran Church.
The review also includes extensive evaluations of benchmarks from various historical periods, including Roman structures in Portugal and Mamluk buildings in Egypt. The research clearly indicates that a combined use of multiple characterization methods yields more reliable results, forming a solid foundation for future restoration projects.
The authors of this important study—Mertcan Demirel, Alican Topsakal, and Muhammet Gökhan Altun—call for immediate attention to these findings, as they could significantly impact the scientific approach to restoration and conservation. The paper is available for review and can be accessed via DOI: 10.1007/s11709-025-1222-3.
As the world grapples with the challenge of preserving cultural heritage, this urgent update serves as a critical reminder of the need for advanced scientific methods in safeguarding our historical treasures. Share this vital information to raise awareness about the importance of preserving our architectural legacy!