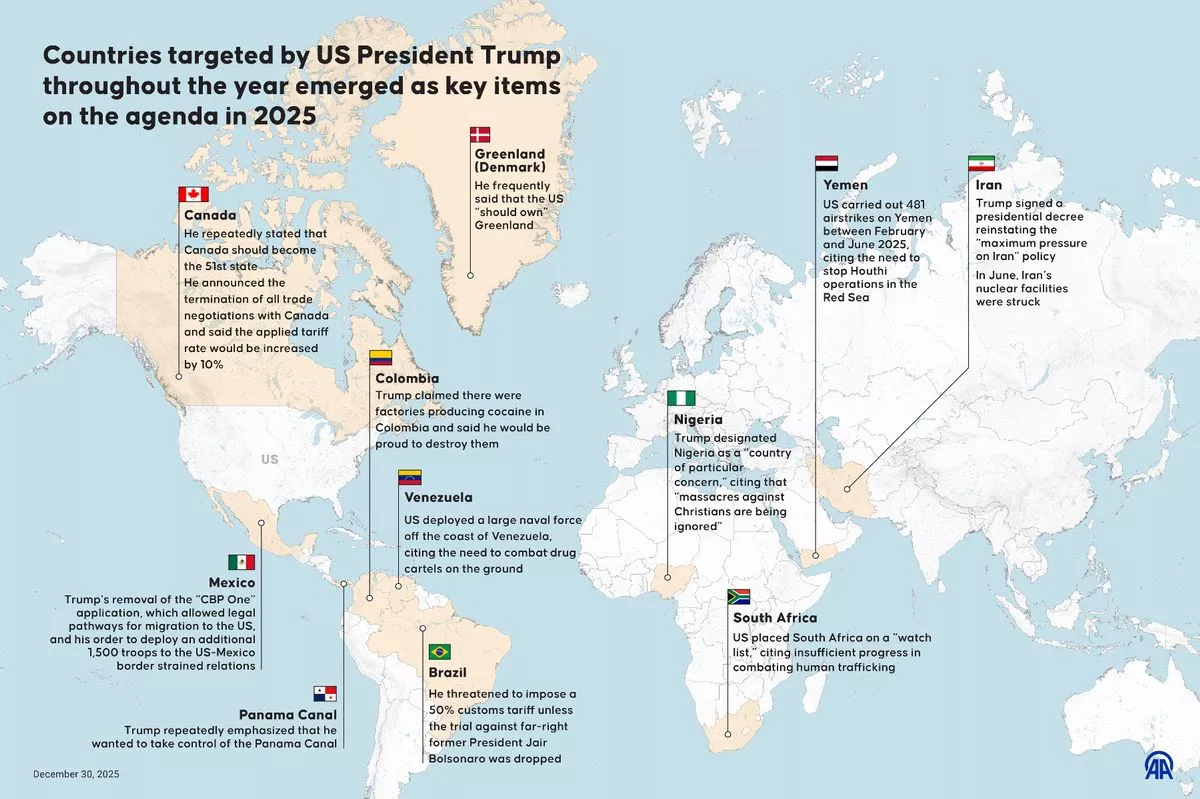
Since his return to the White House nearly a year ago, Donald Trump has implemented a series of controversial policies impacting numerous countries. As the first U.S. president to serve non-consecutive terms in a century, Trump has focused on trade tariffs, immigration restrictions, and military actions that have drawn significant international scrutiny.
One of Trump’s primary strategies has been the introduction of tariffs. Early in 2025, he suggested that Canada could avoid increased taxation by joining the U.S. as the 51st state. In March, he imposed tariffs on Canadian metals, threatening a potential increase of up to 50%. This move prompted a strong response from Ontario Premier Doug Ford, who warned of drastic measures, including shutting off electricity to the U.S. if tensions escalated.
In addition to trade tensions, the Trump administration has expanded its travel ban. Recently, it added seven countries to the list and imposed new restrictions on individuals traveling from fifteen others. In a significant shift, the administration announced that it would no longer issue visas to individuals traveling with documents from the Palestinian Authority.
Trump’s policies have also raised alarms regarding immigration. Following a shooting incident involving two National Guard members in Washington, D.C., he threatened to “permanently pause” all migration from what he termed “third-world countries.”
Throughout 2025, the administration’s approach to Colombia has been particularly confrontational. Trump accused Colombian President Gustavo Petro of facilitating drug production, announcing in October that the U.S. would cease subsidies to Colombia. This relationship deteriorated further with airstrikes against boats in the Caribbean, targeting alleged drug trafficking operations.
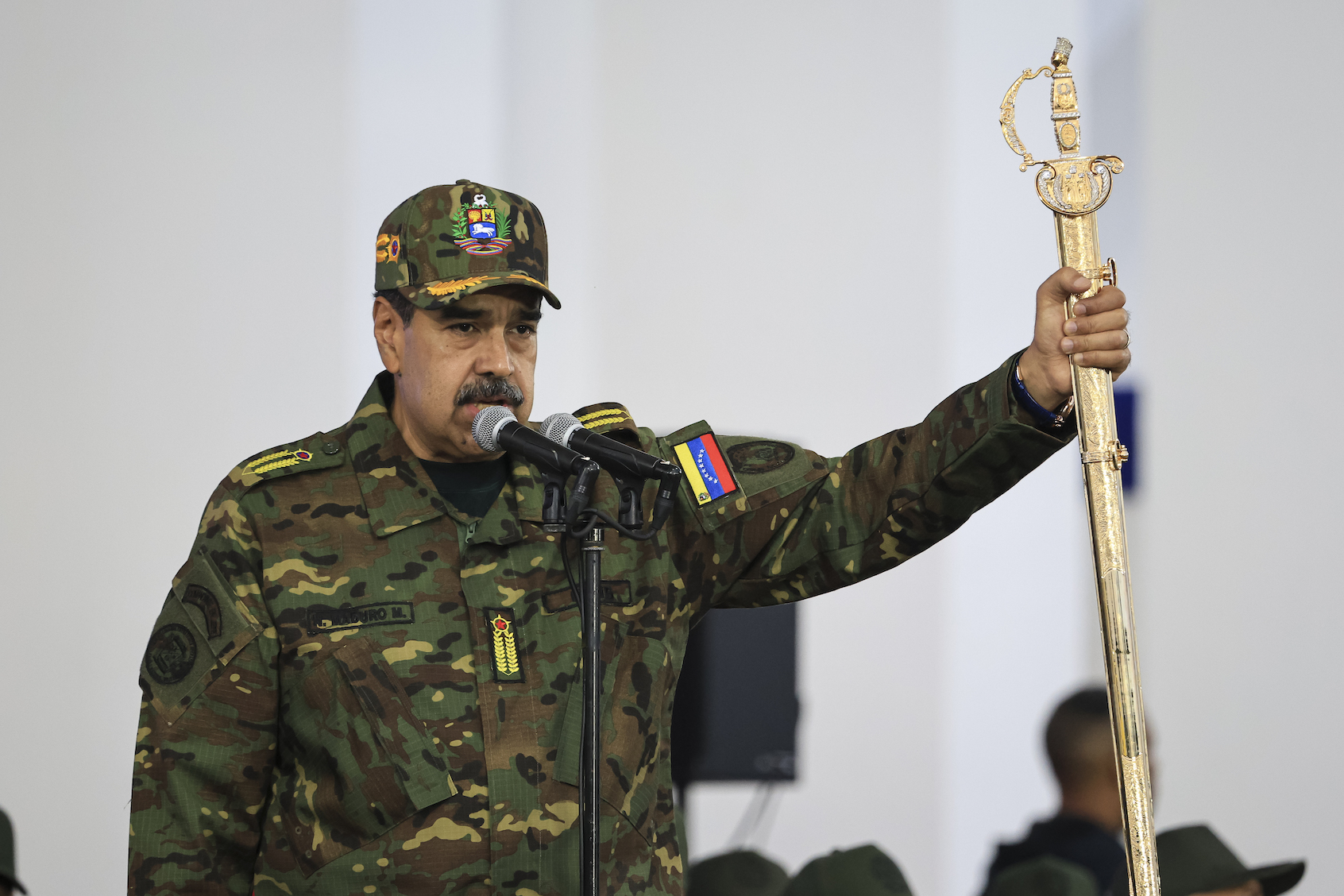
The situation in Venezuela has also become a focal point of Trump’s foreign policy. The administration has refused to recognize Nicolas Maduro as the legitimate president, and the U.S. launched military operations against perceived threats in the region. Critics have described these actions as tantamount to acts of war.
Trump’s relationship with Brazil has shifted dramatically. After initially threatening a 50% customs tariff unless legal proceedings against former President Jair Bolsonaro were halted, discussions with new President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva have improved bilateral relations.
Trump has also made headlines with his comments about Greenland, stating that the U.S. “needs” the territory for national security purposes. His appointment of a special envoy to Greenland has been met with resistance from Prime Minister Jens-Frederik Nielsen, who emphasized the territory’s autonomy and right to self-determination.
In Africa, Trump labeled Nigeria a “country of particular concern,” citing violence against Christians. This rhetoric coincided with U.S. military action against ISIS in Nigeria, which Trump claimed was necessary due to the government’s failure to protect vulnerable populations.
The administration’s stance on South Africa has also raised eyebrows. It was placed on a “watch list” for human trafficking, with the annual Trafficking in Persons report noting insufficient progress in addressing the issue.
Additionally, the U.S. has intensified its military involvement in the ongoing conflict in Yemen, conducting over 480 airstrikes between February and June 2025. These strikes have reportedly resulted in significant civilian casualties, prompting concerns from various human rights organizations.
In the context of Iran, Trump reinstated a policy of “maximum pressure,” aimed at curbing the country’s nuclear ambitions. This culminated in military strikes against Iranian nuclear sites in June, amidst rising tensions linked to the Israel-Iran conflict.
As 2025 draws to a close, Trump’s aggressive foreign policy approach has significantly affected U.S. relations with several nations. The long-term implications of these actions remain uncertain, with critics warning of potential diplomatic fallout.